- accessing the HTML pages of a web biomolecular database containing the data of interest;
- locating the exact position of the data of interest in an HTML page, identified by specific HTML tags;
- extracting these data and those identified by the same HTML tags present in other pages with similar structure;
- performing filtering operations on the extracted data, if needed, and using some data to characterize the other data.
In MyWEST, templates can be created through the Template configuration panel (Figure 1).
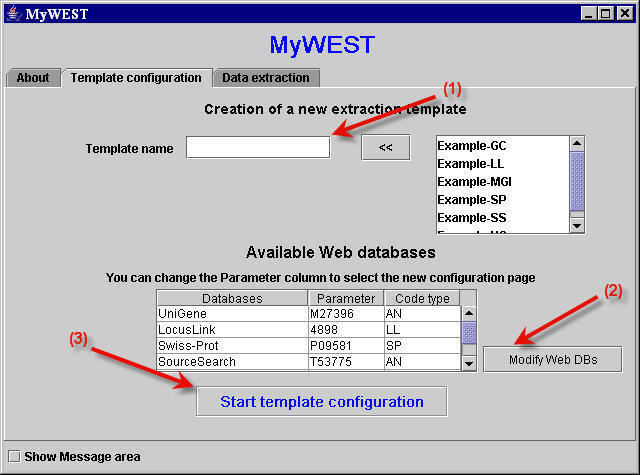 |
| Figure 1. "Template configuration" panel used to create and configure templates. |
In this panel, the user must provide a name for the template to be created, or choose from the list in the top right part of the panel an existing template to modify [click the << button to select it].
The table in the center of the panel shows, in the Databases column, the available web databases, set in the DatabasesURL.txt file, containing in their HTML pages information of interest that can be extracted with MyWEST. The Parameter and Code type table columns show the identification code and code type [e.g. AN: Accession Number, LL: Locus Link ID, UC: Unigene Cluster, ...], respectively, of the clone whose HTML page in the web database is considered as reference page during the template creation. To change the reference HTML page, simply double click on its clone code in the Parameter column and type the clone ID of the new reference page.
The Modify Web DBs button opens a window for the modification of the configuration DatabasesURL.txt file, and allows to add or remove from this file available web databases, or to change their accessing parameters and default HTML reference page. [See here how to configure the DatabasesURL.txt file.]
The Start template configuration button takes to the template-building interface (Figure 2).
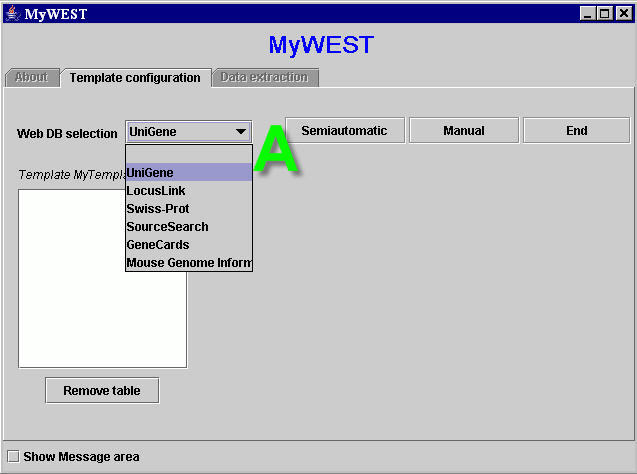 |
| Figure 2. Template building interface. A: available web database menu. |
The reference HTML page set for the selected web database is downloaded from the web and shown in an auto pop-up web browser window. [With some web browsers the user must manually refresh the page visualized in the browser to see the new downloaded page].
Secondly, the user must provide few sequences of characters, selected on a reference HTML page, which can identify the data to extract. This operation varies in relation to the method chosen to create the template. Two template creation modalities have been defined:
- Semiautomatic, for creating templates to extract groups of data structured as they appear formatted on an HTML page;
- Manual, for extracting and structuring sparse data on an HTML page.
By clicking the Change button, advanced users can change the default extraction parameters, stored in the Config.txt file, to customize the extraction performances [see here how]. Specific extraction parameters for each created template are saved in a file (templateName_config.txt) stored together with the template file (templateName.pro) in the MyWEST/templates/ directory.
Semiautomatic template creation
This method permits creating templates for extracting set of data from HTML pages, maintaining the structure the data have in the page.
For each set of data to extract, the user must select three sequences of characters on a reference HTML page.
- The first sequence constitutes an anchor, i.e. a unique sequence of characters on the page. It represents a landmark for locating, inside a page, the HTML structure containing the data of interest to extract.
- The other two sequences of characters are used by the extraction algorithm implemented in MyWEST to identify automatically, within the page, the HTML structure containing the data to extract.
For example, in order to extract from the UniGene database HTML page in Figure 3 the data inside the dashed line, the sequence of characters "SIMILARITIES", unique in the page, can be provided as anchor. The other two sequences of characters must be selected among the data to extract (e.g. "H.sapiens" and "asparagine" or "M.musculus" and "sp:Q61024").
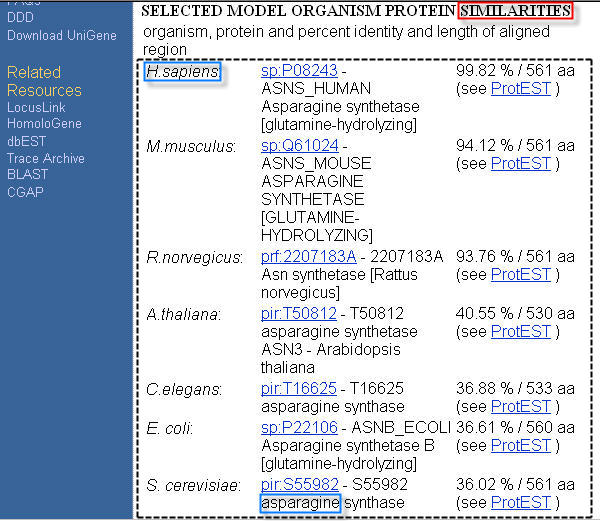 |
| Figure 3. Example of HTML page from the UniGene database. The data of interest to be extracted are inside the dashed line. A sequence of characters that can be selected as anchor is highlighted in green. Other two sequences of characters that can be selected to identify the HTML structure containing the data of interest are highlighted in red |
After selecting UniGene in the Web DB selection menu and clicking the Semiautomatic button (Figure 2), the three selected sequences of characters can be copied from the reference HTML page appeared in the web browser window (Figure 3) and pasted in the correspondent text fields in the Semiautomatic selection area of the template building interface in the MyWEST Template configuration panel (Figure 4).
[Note: for a correct functioning, no blank characters (i.e. spaces) must be present at the end of the sequences of characters pasted in the text fields of the MyWEST interface (Figure 4). If this occurs, when clicking the Catch button a not found warning window appears].
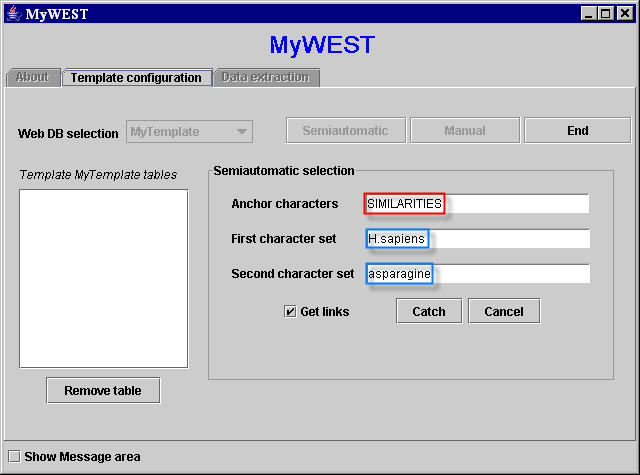 |
| Figure 4. Text fields filled with the three character sequences |
The checkbox Get links enables to extract also names and URLs of links in case present in the HTML page within the extracted data.
Clicking the button Catch, the program analyzes the reference HTML page, automatically searches inside it the three selected sequences of characters, and checks for their unambiguousness in the page.- If not all characters of each of the selected sequences of characters are within the same HTML tag in the page HTML code (i.e. they have not the same appearance), or blank characters (i.e. spaces) are present at the end of the selected sequences of characters pasted in the text fields of the MyWEST template building interface (Figure 4), a not found warning window appears asking the user to check the selected sequences of characters.
- If the sequence selected as anchor is not unique on the page, a Select a unique Anchor warning window appears asking the user to provide a new anchor.
- If the other two selected sequences of characters are not unique, a warning window with the table list of all the sequences of characters in the page equal to the selected sequences appears. The user is asked to unambiguously identify, by selecting the corresponding row in the table list of the warning window, which of the same sequences on the page has actually to be considered (Figure 5). This unambiguous identification is done on the basis of the characters preceding the ambiguous selected sequence on the page (see column A and B, respectively, of the table list in the appeared warning window).
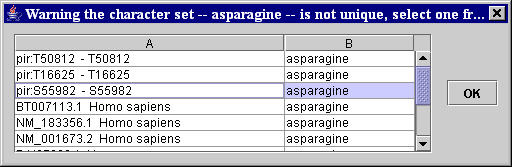
Figure 5. Window for the unambiguous identification in the HTML page of the selected sequences of characters. - If the latter unambiguous selected sequences of characters do not belong to the same single HTML structure in the page containing the set of data to extract, or they are not distinct (i.e. they identify a single data), an Extraction problems warning window appears and the user is asked to check and repeat the selection of the sequences of characters.
[Note: in case a single data (instead of a set of data) extraction is required, the Manual template creation method must be used].
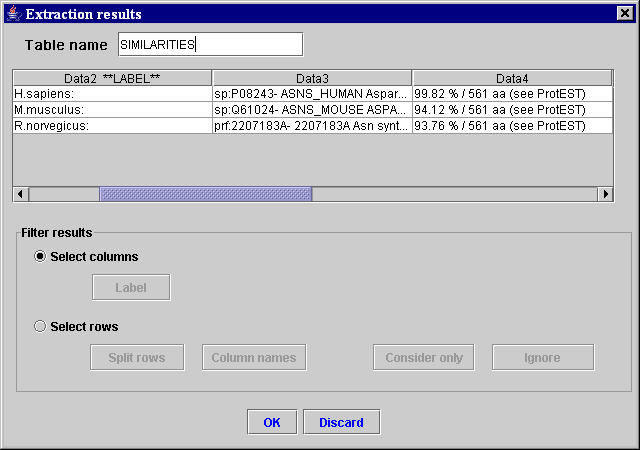
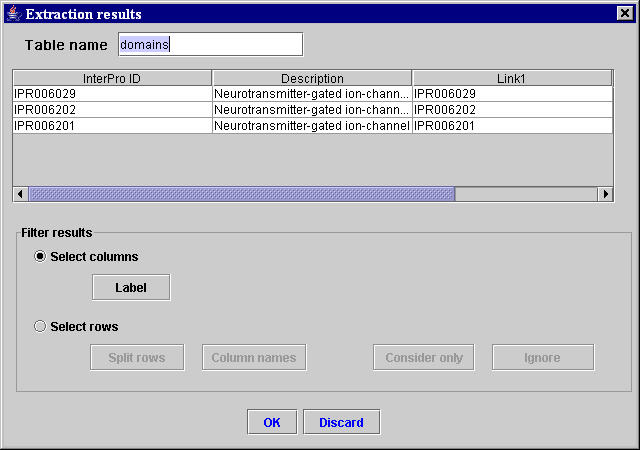
Using the three unambiguous selected sequences of characters, the MyWEST automatically finds the HTML structure containing the second two selected sequences of characters and the data to extract, and defines the relative path in the page from the anchor to the HTML structure with the data to extract. [Afterward, this relative path is saved in the created template together with the anchor and the HTML tag of the HTML structure containing the data to extract (used for correctness checking of the extracted data)]. Then, MyWEST extracts and formats the data identified in the considered reference HTML page and shows them formatted in the extraction result table inside the Extraction results window (Figure 6).
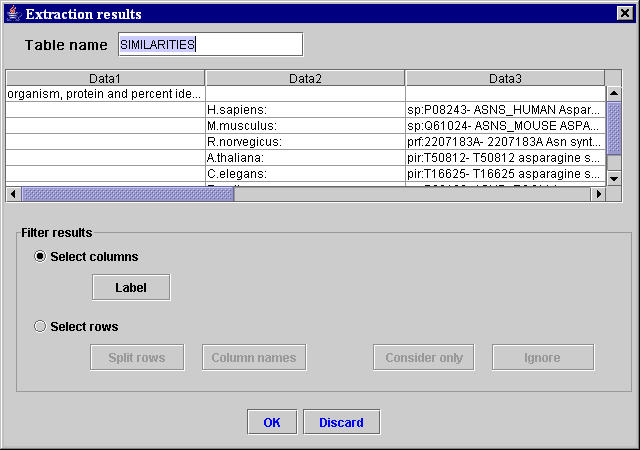 |
| Figure 6. “Extraction results” window containing the result table with the data extracted from the reference HTML page. |
If the extraction is not satisfactory, the user can click the Discard button (Figure 6) and repeat the template creation by selecting more adequate sequences of characters or modifying the extraction parameters.
Using the Semiautomatic template creation method, all data contained in the identified HTML structure are extracted and structured inside the extraction result table, whose structure depends on the formatting and number of data in the HTML structure and on the used extraction parameters.If some of the extracted data can be used to specify others, or not all extracted data are of interest for the specific extraction requirements, it is possible to create a second part of the template to define filtering operations on the extraction result table. Two types of filtering operations can be defined:
- operations on the extracted data
- operations on the result table structure.
The second are useful when some table rows subdivide logically the extracted data in subtables, or when the cells in a table row contain the name of the table column they belong to. In the last case, the names of the extraction result table columns can be assigned automatically, better characterizing the contained extracted data and therefore enabling subsequent more specific queries on all the extracted aggregated data.
Both filtering operations can be defined using the buttons in the Filter results area of the Extraction result window (Figure 6).
- To set an extraction result table column as containing the label values identifying the different table rows, select the Select columns radio button, select the table column to set, and click the Label button. The **Label** tag appears in the set label column name.
- After setting a label column:
- to ignore or to consider only the data in the table rows with specific labels in the label column, select the Select rows radio button, select the only rows to ignore or consider, and click the Ignore or Consider only button, respectively.
- If some table rows subdivide logically the extracted data in subtables, select the Select rows radio button, select a subdividing table row, and click the Split rows button to split the extraction result table in subtables divided by the selected split rows. A new result table is created for each splitting row present in the original result table. All the created subtables are shown one at a time in Extraction results windows similar to that in Figure 6, and on each single subtable it is possible to define all filtering operations.
- If a table row contains the name of the table columns, select the Select rows radio button, select the row containing the table column names, and click the Column names button to assign as name for each table column the value contained in the correspondent column cell of the selected row.
Example 1
Starting from the result table in the “Extraction results” window of Figure 6, to filter and keep only the protein similarities of Homo sapiens, perform as follows.
- Select the Select columns radio button, select the table column Data2, and click the Label button. The **Label** tag appears beside the Data2 column name (i.e. Data2**Label**) showing that the table column Data2 has been set as label column, i.e. as column containing the label values identifying the different table rows.
- Select the Select rows radio button, select the row containing “H.sapiens”, “M.musculus”, and “R.norvegicus” in the label column Data2**Label**, and click the Consider only button. In the result table of the “Extraction results” window only the Homo sapiens, Mus musculus, and Rattus norvegicus protein similarities remain (Figura 7).
Figure 7. “Extraction results” window containing the result table with the data extracted and filtered from the reference HTML page.
Example 2
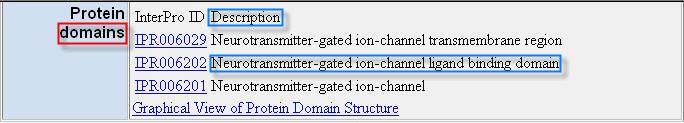
Lets want to extract the Protein domains annotation from the Mouse Genome Informatics database HTML page in Figure 8.
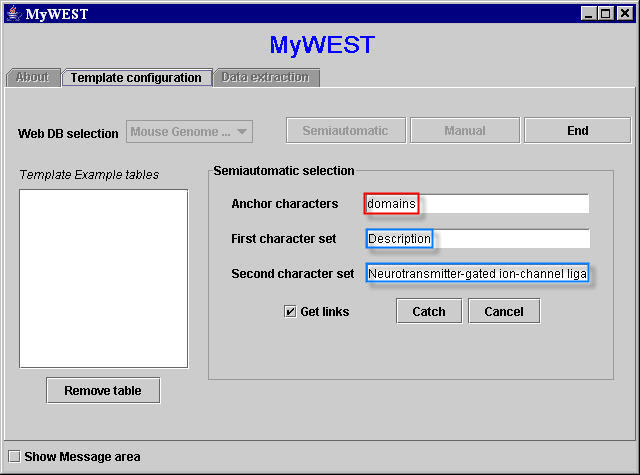
Using a template semiautomatically created, it can be provided the sequence of characters domains as anchor, and the two sequences of characters Description and Neurotransmitter-gated ion-channel ligand binding domain to identify the HTML structure containing the data to extract from the page (Figure 9).
Figure 8. “Protein domains” annotations for the MGI:87895 gene in the correspondent HTML page of the Mouse Genome Informatics (MGI) database.
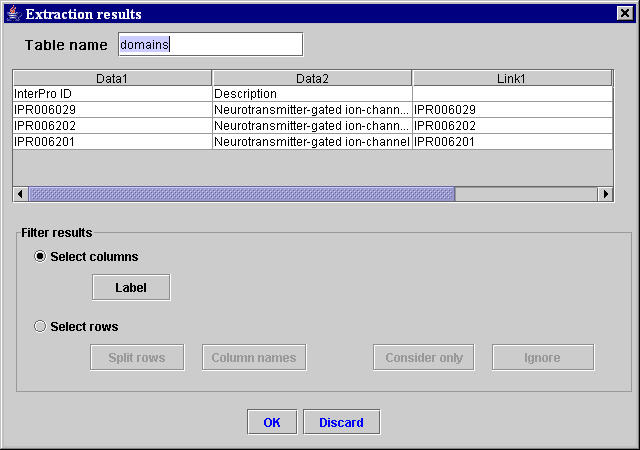
Thus, the Extraction results window in Figure 10 is obtained.
Figure 9. Interface for the creation of semiatomatic extraction templates: text fields with the selected three sequences of characters.
Following, to assign as name for each column of the Extraction results table the value contained in the correspondent column cell of the first row of the Extraction results table:
Figure 10. “Extraction results” window containing the result table with the data extracted from the Protein domains section of the Mouse Genome Informatics HTML page for the gene code MGI:87895.
- select the Select rows radio button, select the first row of the Extraction results table (containing the table column names), and click the Column names button. The names of the result table in the Extraction results window are assigned (Figure 11).
Figure 11. “Extraction results” window containing the result table in Figure 10 with the assigned colum names.
In the Table name text field of the Extraction results window (Figures 6, 10, 11), a name for the extracted and filtered data table can be typed [the default name is the sequence of characters selected as "anchor" for the extracted data].
If the extraction and filtering is not satisfactory, click the Discard button (Figures 6, 10, 11) and repeat the template creation by selecting more adequate sequences of characters or modifying the extraction parameters. Otherwise, click the OK button (Figures 6, 10, 11) and save the created data extraction and filtering template as a template table inside the template file, named "templateName".pro, stored in the MyWEST/templates/ directory.
The name of the new created template table, with some summary information, is shown in the text area on the left side of the main template building interface of the MyWEST Template configuration panel (Figure 4). To delete a created template table, select the template table name appearing in this text area and click the Remove table button.
Through the main template building interface of the Template configuration panel the user can create other data extraction and filtering tables for the considered template, or finish the template configuration by clicking the End button.
Manual template creation
This method permits creating templates for extracting one or several individual data from HTML pages, independently of the way they appear formatted on the page. Thus, it enables creating and customizing extraction result tables choosing the data types to extract and how arranging them in the result table. Templates created with this method are formed of "extraction units", one for each type of data to extract from the HTML page, representing the columns of the extraction result table.
For each unit, the user must select two sequences of characters on a reference HTML page.
- The first sequence constitutes an anchor, i.e. an unique sequence of characters on the page. It represents a landmark for locating, inside a page, the data of interest to extract.
- The second sequence of characters is used by the extraction algorithm implemented in MyWEST to identify automatically, within the page, the HTML structure containing the data to extract.
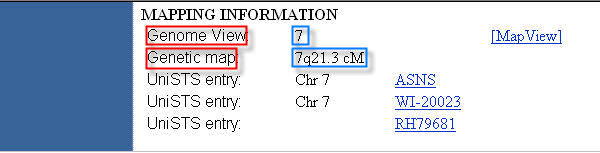 |
Figure 12. Example of HTML page from the UniGene database. The sequences of characters that can be selected as anchors are highlighted in green. The corresponding data of interest to extract are highlighted in red. |
For example, to extract from the UniGene database HTML page in Figure 12 the data inside the two red lines, the user must define two extraction units. The sequences of characters "Chromosome" and "Cytogenetic Position", unique in the page, can be provided as anchors for the first and second extraction unit, respectively. The other sequences of characters must be selected among the data to extract (e.g. "7" and "7q21.3 cM").
After selecting UniGene in the Web DB selection menu and clicking the Manual button (Figure 2), for each extraction unit the two selected sequences of characters can be copied from the reference HTML page appeared in the web browser window and pasted in the correspondent text fields in the Manual selection area of the template building interface in the MyWEST Template configuration panel (Figure 13).
[Note: for a correct functioning, no blank characters (i.e. spaces) must be present at the end of the sequences of characters pasted in the text fields of the MyWEST interface (Figure 13). If this occurs, when clicking the Catch button a not found warning window appears].
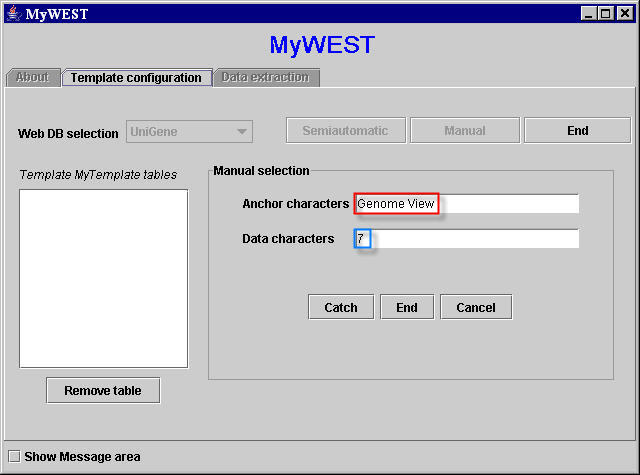 |
| Figure 13. Text fields filled with the two selected sequences of characters for the first considered extraction unit |
- If not all characters of each of the selected sequences of characters are within the same HTML tag in the page HTML code (i.e. they have not the same appearance), or blank characters (i.e. spaces) are present at the end of the selected sequences of characters pasted in the text fields of the MyWEST template building interface (Figure 13), a not found warning window appears asking the user to check the selected sequences of characters.
- If the sequence selected as anchor is not unique on the page, a Select an unique Anchor warning window appears. The not unique sequence of characters selected as anchor is considered as label for the data to extract, and the user is asked to provide a new anchor and to unambiguously identify, by selecting the correspondent row in the table list of the appeared warning window, which of the first anchor selected same sequences on the page has actually to be considered as label for the data to extract (Figure 5).
- If the other selected sequence of characters (that identifying the data to extract) is not unique, a warning window with the table list of all the sequences of characters in the page equal to the selected sequence appears. The user is asked to unambiguously identify, by selecting the correspondent row in the table list of the appeared warning window, which of the same sequences on the page has actually to be considered (Figure 5).
All unambiguous identifications are done on the basis of the characters preceding on the page the ambiguous selected sequence (see column A and B, respectively, of the table list in the appeared warning window (Figure 5)).
Using the two unambiguous selected sequences of characters, the MyWEST automatically finds the data to extract, and defines the relative path in the page from the anchor to the HTML structure with the data to extract. [Afterward, this relative path is saved in the created template together with the anchor and the HTML tag of the HTML structure containing the data to extract (used for correctness checking of the extracted data)]. Then, MyWEST extracts the data identified in the considered reference HTML page for the extraction unit and shows them in a Selection results window (Figure 14).
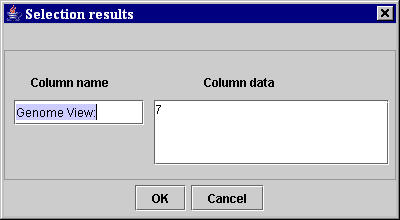 |
| Figure 14. “Selection results” window containing the data extracted from the reference HTML page for the specific extraction unit. |
In the Column name text field of the Selection results window (Figure 14), a name for the extraction unit (a data column of the final extraction result table) can be typed [the default name is the sequence of characters selected as "anchor" for the extraction unit].
If the extraction is not satisfactory, the user can click the Cancel button (Figure 14) and repeat the template extraction unit creation by selecting more adequate sequences of characters or modifying the extraction parameters for the entire template. Otherwise, by click the OK button (Figure 14) finish the extraction unit creation and go back to the Manual selection area of the template building interface in the MyWEST Template configuration panel (Figure 13) where a new extraction unit for the building template can be created.
When all extraction units have been created, by clicking the End button in the Manual selection area of the template building interface in the MyWEST Template configuration panel (Figure 13) all extraction units created are shown formatted in the extraction result table inside the Extraction results window (Figure 15).
[ATTENTION: by clicking instead at this time the End button in the top right part of the template building interface in the MyWEST Template configuration panel (Figure 13) the template creation is ended without saving the creating template.]
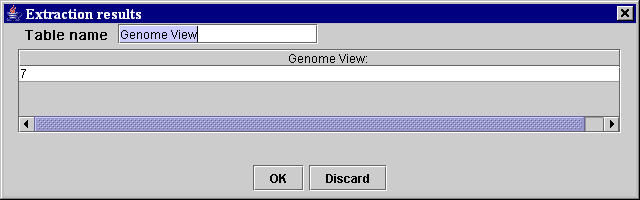 |
| Figure 15. “Extraction results” window containing the data extracted from the reference HTML page for all created extraction units. |
If the extraction is not satisfactory, click the Discard button (Figure 15) and repeat the creation of all template extraction units by selecting more adequate sequences of characters or modifying the extraction parameters. Otherwise, click the OK button (Figure 15) and save the created data extraction template as a template table inside the template file, named "templateName".pro, stored in the MyWEST/templates/ directory.
The name of the new created template table, with some summary information, is shown in the text area on the left side of the main template building interface of the MyWEST Template configuration panel (Figure 4). To delete a created template table, select the template table name appearing in this text area and click the Remove table button.
Through the main template building interface of the Template configuration panel the user can create other data extraction tables for the considered template, or finish the template configuration by clicking the End button in the top right part of the panel.